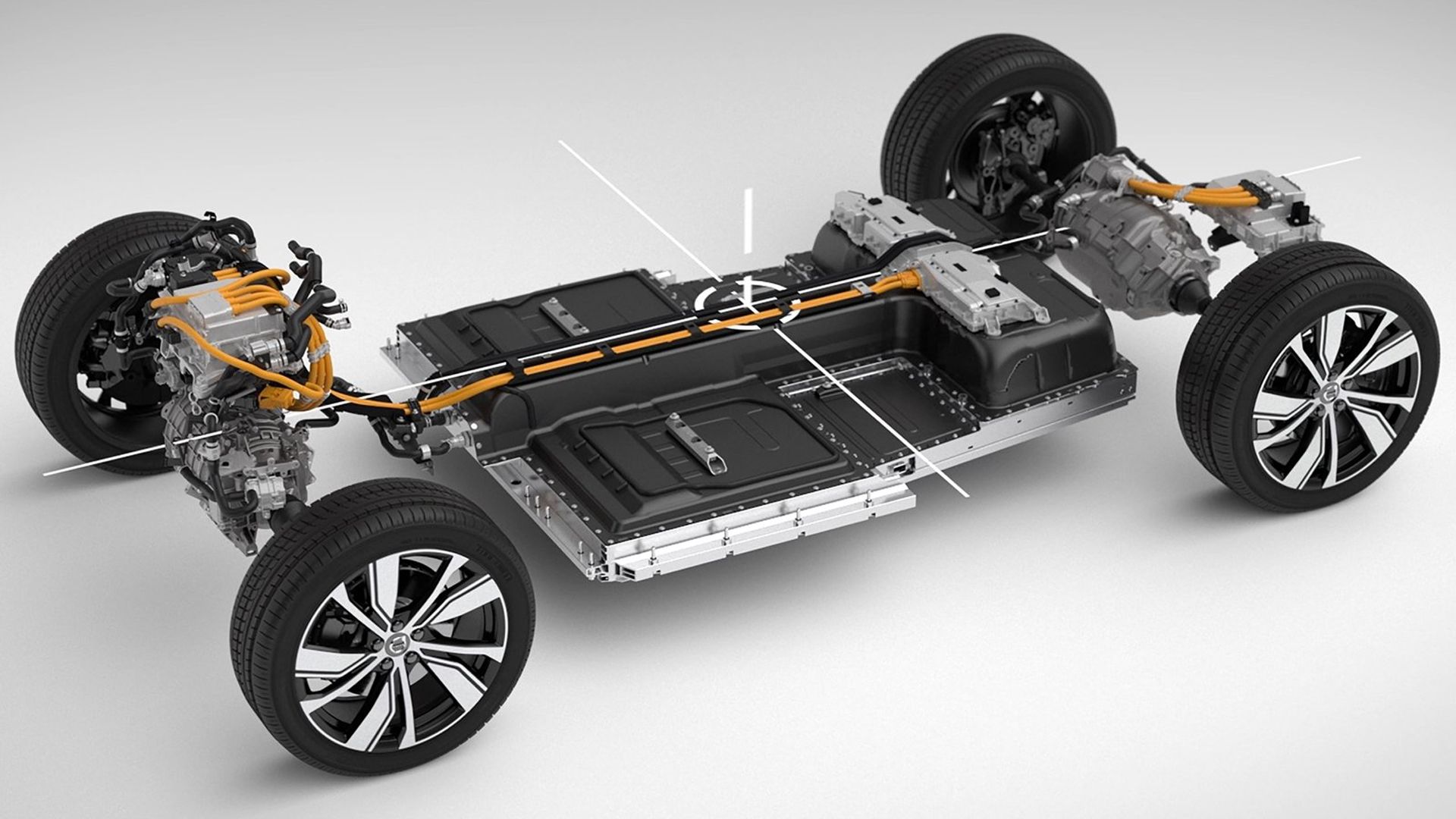
We've always only heard a lot about the environmental benefits of electric vehicles, and although they indeed produce fewer emissions than gas-powered cars, what you may not know is that the environmental impacts of these electric vehicles go far beyond just the tailpipe. What's more, the production of electric vehicle batteries consumes a lot of energy. For example, the manufacturing of a Tesla Model S battery requires the equivalent energy usage of 50 homes. In addition to this, removing these raw materials causes soil degradation, biodiversity loss, damage to ecosystem functions, water shortages, and increases global warming. When evaluating the greenhouse gas emissions from electric vehicle batteries, there are several different factors to consider, from lithium-ion mining to electric grid power production, to battery manufacturing and disposal.
Although some obstacles still exist in terms of electric vehicles going mainstream (such as costs to manufacturing), more people will keep switching from internal combustion engines to simply plugging in at home. Electric vehicles are becoming more and more popular, and that's a good thing! But their batteries come with their own set of environmental impacts. It's important to understand those while we're rushing to make the switch to electric. Although electric vehicles produce zero emissions while driving, the manufacturing and disposal of the batteries can have a significant impact on greenhouse gas emissions.
10 EV Battery Production Takes A Lot Of Energy And Generates Significant Emissions

When you're driving around in your electric vehicle, it's easy to forget that the battery in your car is a small power plant. Because electric vehicle batteries are so large and require a lot of energy to manufacture, their production generates significant greenhouse gas emissions. The production of lithium-ion batteries accounts for 10% of all electric vehicle emissions. When building a car battery, especially in a factory powered by fossil fuels, the kind found in places like Germany, emissions from the factory could be as much as 74% more C02 than what could be reduced when building a conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) car. To manufacture an SUV battery of 500 kilograms (1,100 pounds), the factory ends up pumping out significantly more climate-warming gases than an ICE car.
9 Lithium Mining Process Damages And Contaminates Ecosystems

The main component of electric car batteries is lithium-ion. The mining of this substance is known to generate a lot of toxic pollution. Although it is known that all forms of extraction of resources are harmful to the environment, the mining and processing of lithium is very energy-intensive and tends to be done in ways that are very damaging to the environment. In South America, where the salt flats for lithium are located are mainly arid territories. Water is important for the livelihoods of the local communities, but mining not only consumes but contaminates and diverts these scarce water resources away from these communities. Sometimes, 2.2 million liters of water is used to produce one ton of lithium, which makes mining activities consume as much as 65% of the water from lakes, ponds, and the like.
8 Manufacturing Process Releases Harmful Pollutants Into The Air

Now, electric vehicles are the best step forward in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, but as we have established, the current model of manufacturing of their lithium-ion batteries still produces harmful pollution, a problem that needs to be resolved. In the process of extracting and refining of lithium, cobalt (which is one of the major metals that make it work), and the other metals that are used in battery production often release harmful and very dangerous air pollutants, which include sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxide, and carbon monoxide. In addition to this, the chemical reactions that take place during the production of these batteries also release toxic chemicals into the air. Some of these toxic chemicals are hydrogen fluoride and nickel oxide. These pollutants are known to cause respiratory problems, damage to the environment, and at times, even fatalities.
7 Charging Via The Grid Increases Demand For Dirty Energy Sources
While electric vehicles (EVs) may reduce emissions at the tailpipe, the energy used to power them can still be known to contribute to climate change. To charge the batteries of these electric vehicles, they have to be plugged into the grid whether at home, work, or in a charging station. This means that the energy used by EVs still largely depends on the kind of electricity generation plants that are powering their charge. Unfortunately, many countries still use the usual dirty sources of energy like coal and natural gas—which have always increased greenhouse gas emissions. So, while it's a fantastic idea to switch over to an electric vehicle, it's important to consider where the electricity powering and charging it is coming from, how much energy—and what kind of energy—it is using, and efficient alternatives. This is one of the reasons Toyota is so interested in Hydrogen as an alternative fuel.
6 Poor Disposal Of Spent Batteries Release Toxic Chemicals
Another major environmental impact of electric vehicle batteries is their disposal. Whenever electric vehicles reach the end of their life cycle, they need to be properly recycled because they can also release hazardous gasses. This is important because they can also cause health and environmental hazards. Not all electric vehicle batteries are recycled regularly. This usually leads to the continuous accumulation of all the spent batteries in landfills, though this is an ongoing battle, with manufacturers like Tesla leading the way. Batteries that aren't recycled properly, however, end up discarded without proper treatment. When these spent EV batteries are not properly disposed of, chemical pollutants which make up their core such as lead, nickel, cobalt, and lithium could enter the environment and can harm both wildlife and human health. This is why manufacturers need to ensure that spent batteries are disposed of properly through recycling centers to help protect our environment from toxic chemicals.
5 Valuable Materials In Electric Vehicle Batteries Aren't Recycled
As previously discussed, electric vehicle batteries contain a minefield of valuable materials that can be recycled. This unfortunately isn't done often enough. In this recycling process, the old battery cells need to be disassembled, and the components should be separated into different materials like copper, nickel, cobalt, and aluminum. These materials can be reused in new products. This recycling process in electric vehicle batteries is a very important step towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions from mining and the production of new materials that could otherwise have been derived from spent cells as it decreases the need for mining new materials. The process keeps these valuable materials out of landfills and circulates them within the economy. Recycling these batteries also reduces energy consumption from cell production by up to 80% and is a win-win for us all.
4 Battery Storage Facilities Can Cause Environmental Hazards
A major environmental issue with electric vehicles is the storage and disposal of lithium-ion batteries at the end of their life cycle. If not properly disposed of, the battery storage facilities where they are can create hazardous waste. It is also important to consider where these sites are located to make sure that hazardous substances are not released into the environment. If a storage facility is sited in a location with a fragile ecosystem, it would have terrible consequences. In addition to this, when storing and disposing of batteries, proper safety protocols must also be followed to prevent unintended contact with hazardous materials. These and a few more are the considerations that must be taken into account when evaluating the environmental impacts of electric vehicle batteries, to ensure sustainable electric vehicle use and reduce any potential hazards.
3 They Have Higher Lifetime Emissions Than Gasoline Cars.

When calculating the volume of electric vehicles needed on the roads and the number of batteries that need to be built to power them, remember the processes these batteries go through before they enter these vehicles, and you'd realize that electric vehicles may have higher lifetime emissions than gasoline cars. The manufacturing process with which electric vehicle batteries are produced can produce more emissions than those associated with producing internal combustion engines. This mainly is because of the large quantity of energy required to mine, manufacture, process, store, and transport lithium-ion batteries. However, if the manufacturing process is optimized and these hazards are controlled, in terms of overall lifetime emissions, electric vehicles still come out ahead because their tailpipe emissions — which are the CO2 emissions while driving — are much lower/insignificant compared to those of gasoline cars.
2 EV Batteries Have A Significant Well-to-Wheels Impact
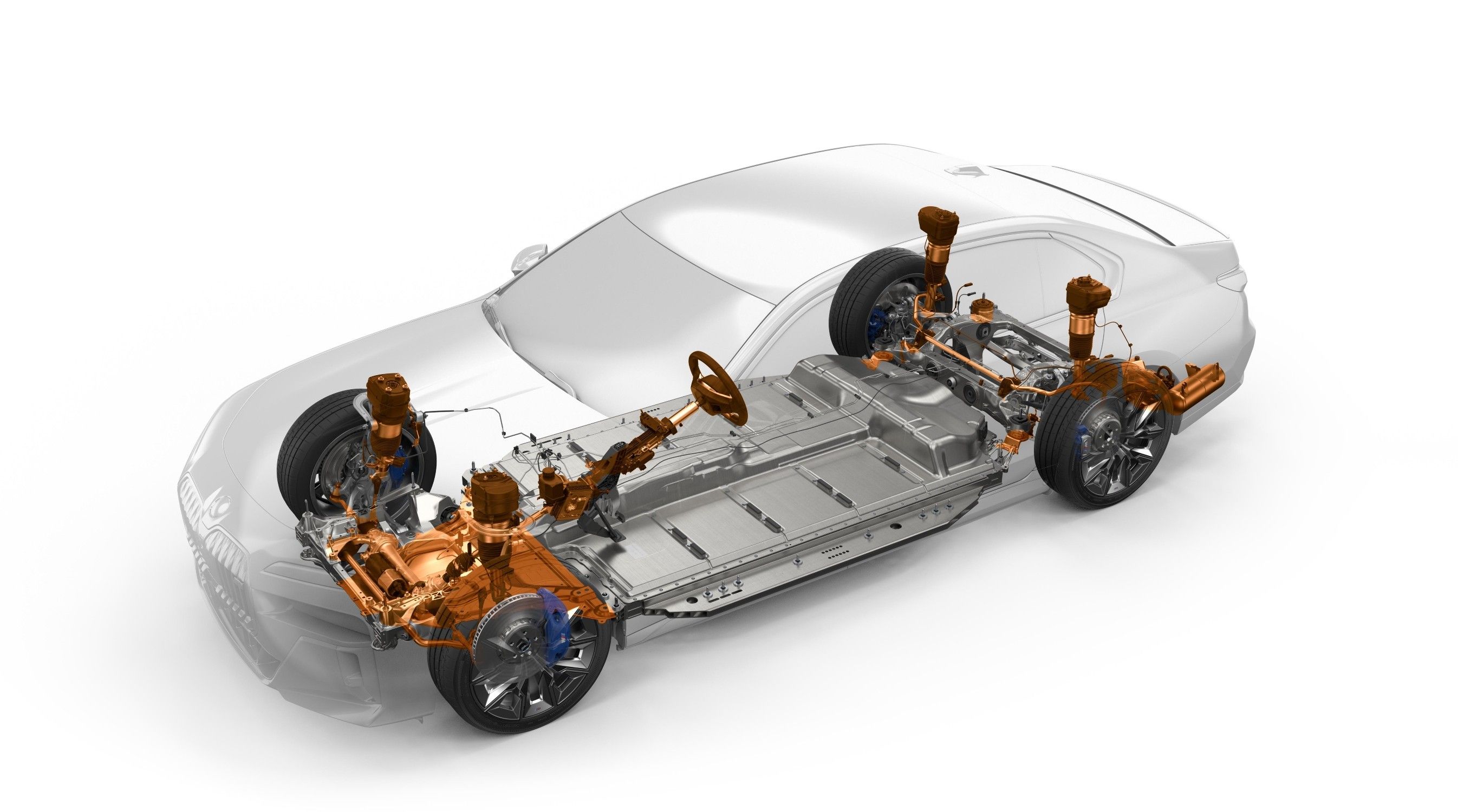
Electric vehicle batteries can reduce tailpipe emissions significantly, but their well-to-wheels impacts are significantly more complex. From the mining process which is dangerous to the environment, to their manufacturing which is mostly done in factories relying on dirty energy sources, to the electric grid production and their disposal at the end of their life cycle, their overall effect on greenhouse gas emissions must be taken into account. The good news is with regulations springing up regularly and with improving advanced battery technologies, the sustainability of electric vehicles will improve as time goes on. Relying only on electric vehicles to reduce net greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change isn't the solution. We will need a combination of strategies such as refinement of the mining process, improved energy efficiency in other industries, electrification of transport, and electricity generation decarbonization.
1 Reducing Or Offsetting Their Greenhouse Gas Emissions Is A Must

Over the years, battery technology has improved greatly. Lithium-ion batteries have more capacity to produce electricity when they are being charged and much lower internal resistance than their predecessors. This new technology presented the opportunity of making transportation electrification a success. In the world of EVs, its important efficiency is improved on in all sections of the battery production process. To make the process of manufacturing these batteries more environmentally friendly, there are two possible paths we can take. Companies involved should invest time and resources into doing things more efficiently, so they use fewer raw materials without losing battery capacity or power. Although it's not guaranteed, it is the most likely path to take. Another possibility is to invent a new, cleaner battery technology that won't use lithium at all. This also isn't guaranteed.