Lithium-ion batteries have played a major role in the development of modern society. It makes possible everything from the devices in our pockets to the electric cars that we drive. The Global EV industry is growing at a rapid pace and the Solid State Battery promises to transform the space by offering lighter, safer, and much more efficient energy storage solutions than outgoing Lithium-ion batteries. Longer lifespans and smaller sizes also mean that Solid State Batteries have the potential to drastically reduce the e-waste generated by expended batteries. The technological and environmental implications of this battery technology could be groundbreaking and hold the potential to revolutionize the EV industry.
What Is A Solid State Battery?
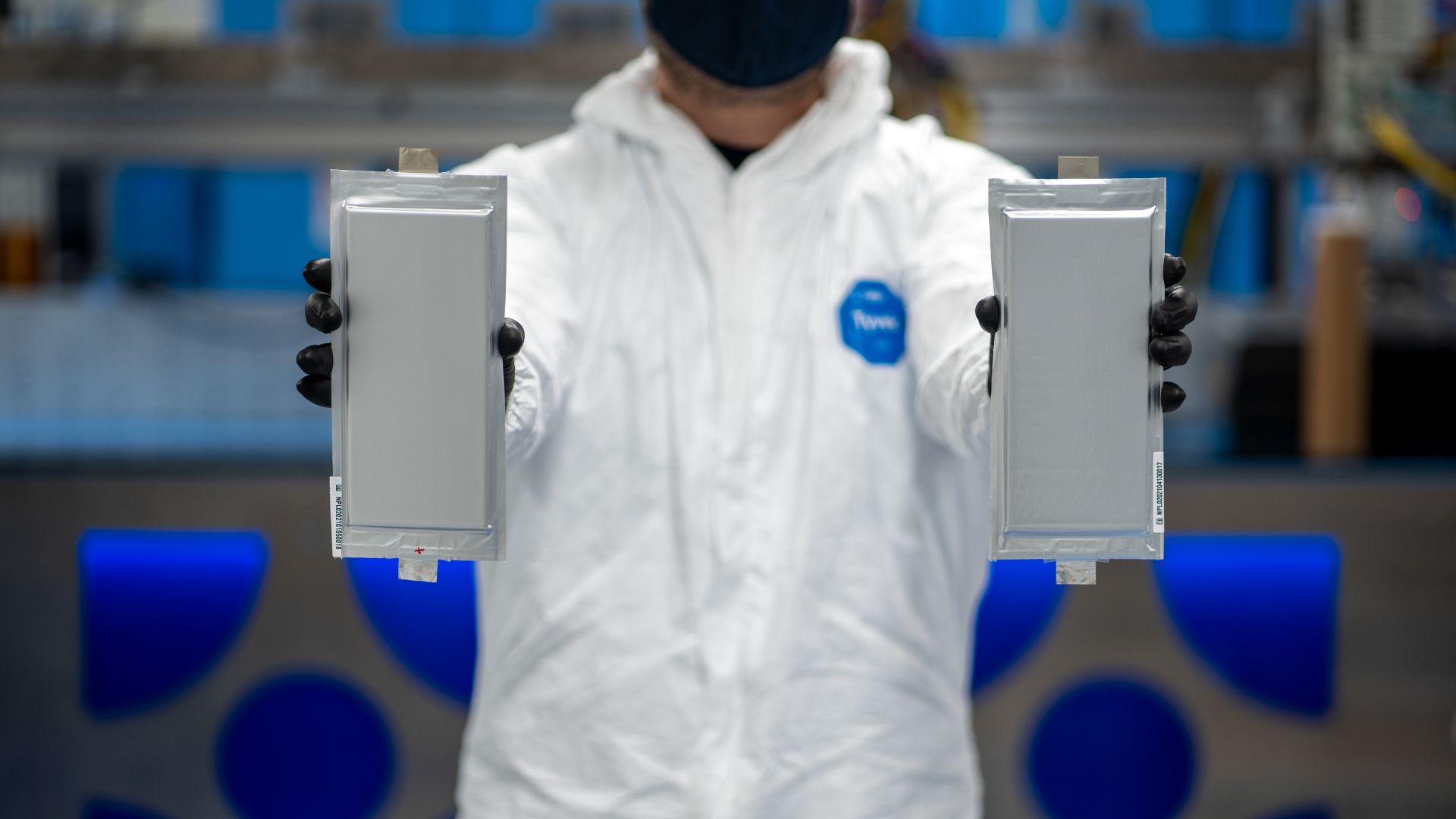
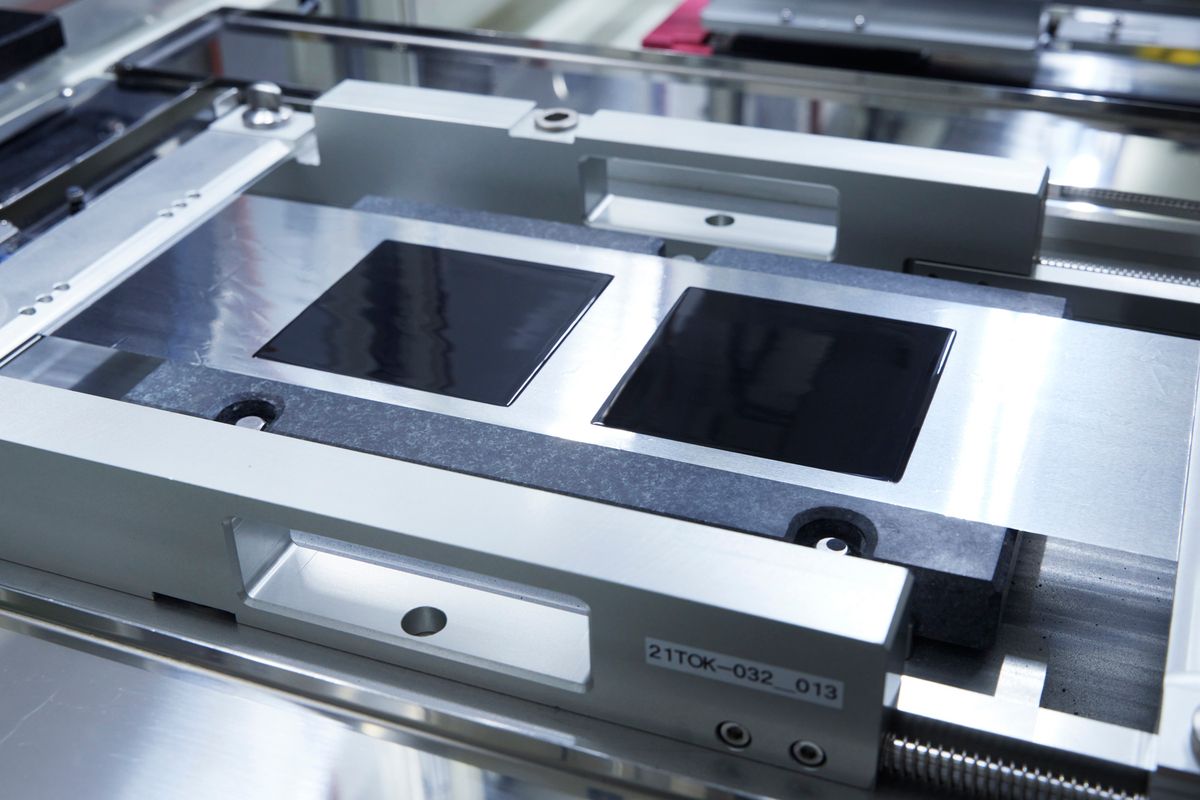
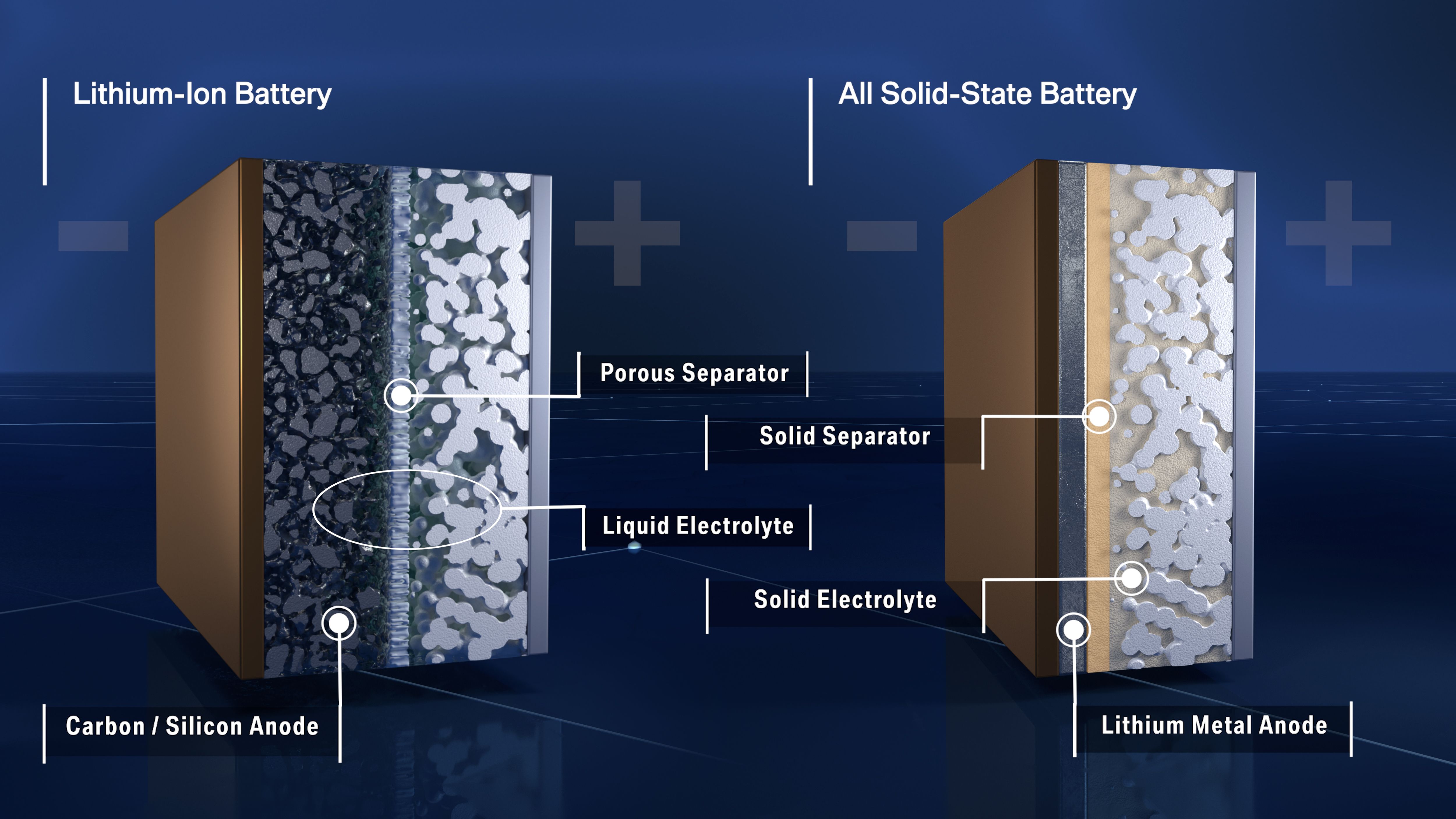
A conventional Lithium-Ion battery such as the ones found in mobile phones and laptops uses a liquid or polymer gel using made using materials like glass, sulfites, and ceramics. A Solid State Battery (SSB), as the name suggests, uses a solid electrolyte material. The electrolyte is the conductive layer that facilitates the flow of electrons from the cathode which is the positive terminal to the Anode which is the negative terminal. Apart from packaging and safety benefits, a solid electrolyte enables the use of other anode materials like Lithium metal which drastically increase the battery's energy density.
History Of Solid-State Batteries
The search for viable Solid State Battery technology has been going on for well over a century and the first foundations of this concept can be traced back to Michael Faraday who was the first to discover 'solid electrolytes' in the 1800s. His battery comprised solid electrolytes made out of silver sulfide and lead fluoride. By the 1950s, this technology started seeing some real-world applications in electrochemical systems. By 1990, researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory developed a brand-new type of solid-state battery and that technology went on to become the basis for thin-film Lithium-Ion batteries.
Solid State Batteries Are Safer Than Li-ion Batteries
The liquid electrolyte solution found in traditional Lithium batteries is tricky to store and improper packaging could lead to issues like dendrite formation within the battery during charging. Dendrites can be defined as stalactite formations that grow from the surface of the anode. These dendrites can not only reduce the battery's capacity but can also short-circuit the cell by puncturing the liquid electrolyte partition, causing the battery to explode. Solid-state batteries with their solid electrolyte, are expected to provide greater safety and performance in comparison to lithium-ion batteries which presently power electric vehicles and have a liquid electrolyte. The risks associated with existing battery technology used in EVs include High flammability, risk of leaking fluid, and Electrolytic decomposition at high voltages, all of which can be addressed by solid-state batteries.
Solid-state Batteries Possess Higher Energy Density
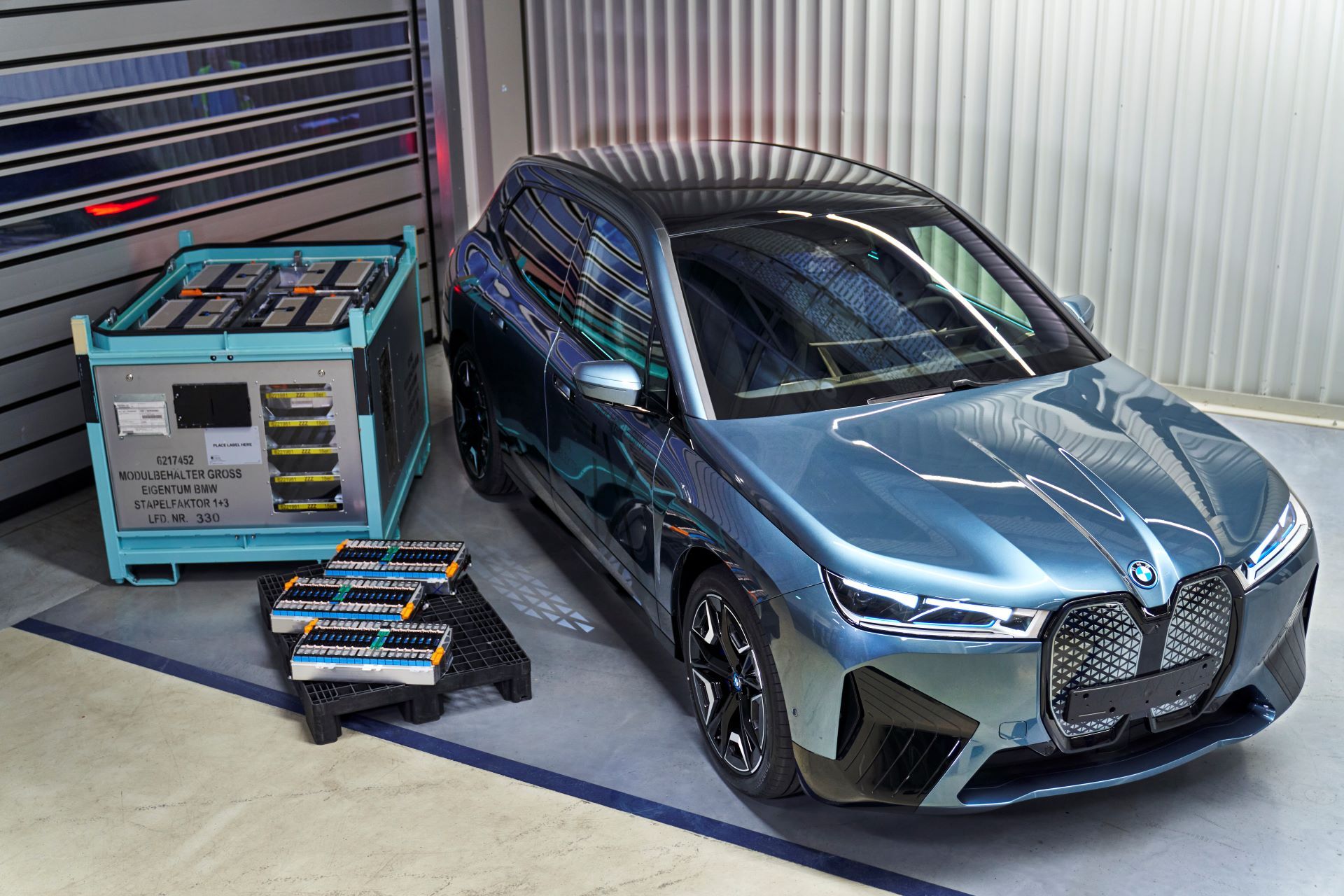
Many big automakers such as BMW, VW, Hyundai, Nissan, and more have invested millions in the R&D of Solid State Batteries over the last decade. This push from automakers is because of the major advantages of SSBs over existing Li-Ion tech. SSBs have a significantly higher energy density compared to conventional Lithium batteries. That allows automakers to store more energy per kilogram, which results in either reduced size and weight or allows the battery to pack much higher energy and deliver a significantly higher range than a similar-sized Lithium-Ion battery.
Their capacity and ability to deliver peak charge also deteriorate with time and use. Lithium-ion batteries also require external cooling which can take up precious space and energy. So the solid electrolyte is not only safer but also results in a higher cell-to-pack ratio, lighter vehicles, higher energy, and power density, extended range and fast charging.
Sold State Batteries Have Longer Lifespan
In addition to the improvements in energy density, Solid State Batteries also promise to offer a significantly longer lifespan than regular Lithium-ion Batteries. Toyota is working with Panasonic to develop Solid State Batteries and has gathered over 1,000 patents in SSB technology to make batteries that retain 90-percent battery capacity after 30 years of use. Li-Ion batteries such as the ones used in EVs can lose up to a third of their capacity within a decade. This shorter lifespan combined with their relatively larger footprint compared to Solid State Batteries means they will fill up landfills much faster than comparative SSBs. With EVs projected to grow to 8.4 million units by 2025, the amount of E-waste generated can be significantly reduced by using Solid State Batteries.
What Is The Environmental Impact Of Solid-State Batteries?
The smaller footprint and longer lifespan of Solid State Batteries are not only good from a packing and efficiency standpoint, but Solid State Batteries also hold the potential to reduce the environmental impact of batteries. A recent study commissioned by Transport & Environmental from Minviro compared Solid State Batteries to existing Battery technology. This study also indicates that Solid State Batteries hold the potential to reduce the carbon footprint of EV batteries by two-thirds. The study also says Solid State Batteries can reduce the climate impact of batteries by 39-percent compared to outgoing Lithium-ion batteries, provided the raw materials are sustainably sourced. This is just the boost required to take the EV industry further and make it a more compelling alternative to IC technology.
Why Are Solid State Batteries The Next Big Thing?
The research into solid-state batteries started taking off in 2015, giving rise to some key players and advancements in the field of SSBs. Samsung has developed an SSB prototype that solves the dendrite problem by using anodes made of silver carbon composite. Ilika Technologies Ltd, pioneers in solid-state battery (SSB) technology, announced it is leading a 24-month, £8 million Faraday Battery Challenge collaboration project.
Volkswagen got a five-percent stake in Quantumscape and its SSB technology. QuantumScape released its performance data in December 2022 which revealed that their SSBs have a staggering Volumetric energy density of more than 1,000 Wh/L while the best batteries used in existing EVs go as high as 700 Wh/L. In addition, QuantumScape's SSB can recharge to 80-percent capacity in 15 minutes and retain 80-percent of its capacity after 800 charging cycles. Volkswagen estimates that SSBs could be powering your EVs, as early as 2024 while Toyota estimates its first SSB-powered EVs will start rolling out by 2025. So it's safe to say that Solid State Batteries are the future of electric mobility.